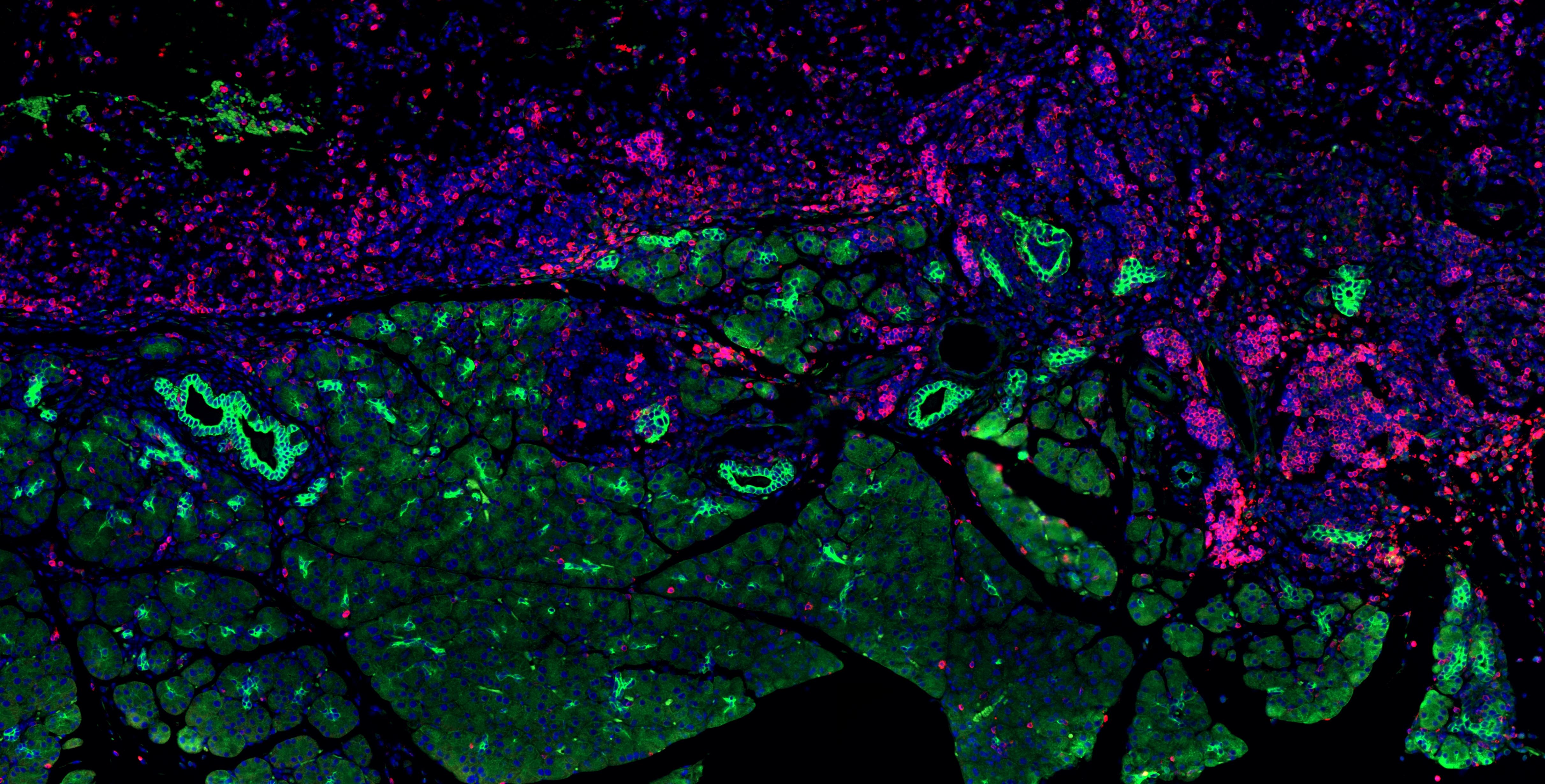
Pancreatic Cancer
Tumors are not just cancer cells, but include many other cell types, including immune cells. A tumor’s DNA makeup can profoundly influence the number and types of immune cells in the tumor microenvironment, but this association has not been well-defined in PDA. We found that a tumor's genotype can influence the composition of the immune cells surrounding it, which can, in turn, affect sensitivity to cancer therapy.
We are investigating how mutational variation in pancreatic tumors contributes to therapy resistance. Although tumor genotype is not currently utilized for selecting patients for immunotherapy (apart from the 1% of PDA patients who are MSI high), we aim to provide preclinical evidence for patient stratification in clinical trials based on tumor genotype and/or immunophenotype. Our goal is to inform the development of personalized medicine regimens!
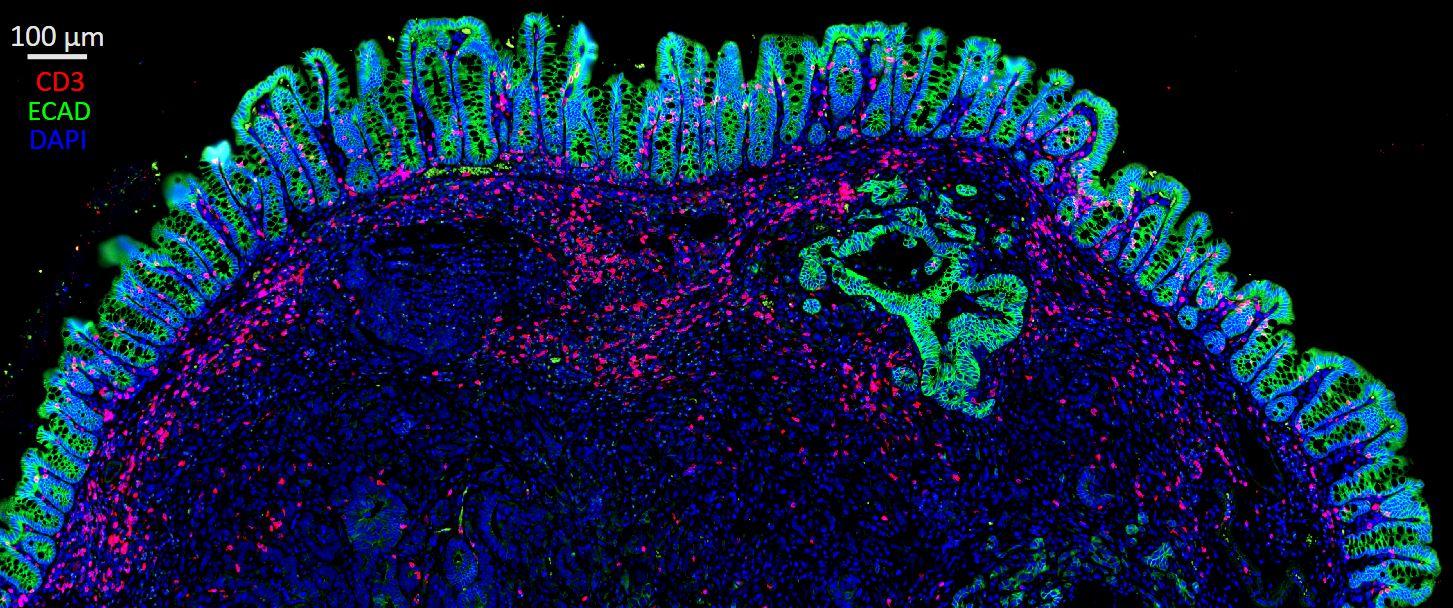
Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer is the third most common cancer affecting both males and females in the United States. Although we have identified many of the genetic and environmental changes that contribute to the development of colon cancers, we still have very few effective treatment options. Understanding how tumor mutations and their surrounding cells cause tumor development is essential for the creating better drug therapy. Several differences can be seen in the colon cancers that begin on the left side, in the descending and sigmoid parts of the colon, compared to those that occur on the right side, in the ascending and cecum portions of the colon. The differences between left-sided and right-sided colon cancers include why and how the cancer developed, and the cancer’s aggressiveness and how well it responds to usual chemotherapy regimens. We are using a unique set of tools to address these fundamental problems, including 3D organ-like cultures (organoids) isolated from mouse colon.
Read about our work in the news section!